
Logistics Management: Definition, Functions, and Benefits
Logistics management jobs in the UK are vital to ensuring the efficient flow of goods, services, and information across the supply chain. These roles encompass a variety of responsibilities, including inventory management, transportation, warehousing, and distribution.
According to data from the Chartered Institute of Logistics and Transport (CILT), the logistics sector contributes over £127 billion to the UK economy annually and employs around 2.5 million people. As the industry embraces digital transformation, the future of logistics management looks promising, with increased demand for professionals skilled in automation, data analytics, and sustainability practices. Emerging technologies, such as AI and IoT, are set to revolutionise logistics operations, enhancing efficiency and reducing costs. Logistics company like DHL is in charge of investing in innovative solutions to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market. With the rise of e-commerce and the need for more agile supply chains, logistics management roles in the UK are expected to grow significantly, offering diverse career opportunities.
In this article, we’ll have a deeper look at logistics management. So let’s start our learning journey without wasting time.
Table of Contents
Definition of Logistics Management
Logistics management, meaning the planning, implementation, and control of the efficient and effective forward and reverse flow and storage of goods, services, and related information from the point of origin to the point of consumption, is a key component of supply chain management. This critical aspect of business is essential for maintaining smooth operations, from order processing to the physical distribution of products. It demands strategic planning and data driven decisions to ensure that inventory levels, shipping costs, and labour costs are balanced to meet customer demands without incurring unnecessary expenses.
In NextGen Learning, we have a course titled Logistics Management at QLS Level 5 for enthusiasts looking for logistics jobs or anyone wants to get a good idea on logistics management and start their own business.
Seven Essentials Logistics Functions
Logistics management is developed around seven key functions that are essential to the success of any logistics provider. These logistics functions, including inventory control and logistics transport, are the foundation for a smooth supply chain operation, ensuring efficiency in delivering products to customers while upholding payment and delivery terms. These logistics services are vital across industries such as e-commerce and manufacturing, helping businesses maintain a competitive edge.
Order Processing in Logistics
Order processing is a crucial logistics function that connects inventory management to customer needs. It involves receiving, fulfilling, and verifying customer orders and is the first step in logistics transport. Effective order processing boosts customer satisfaction and loyalty, as it ensures that logistics providers can meet customer demands through efficient inventory levels.
Product and Material Handling in Logistics
Product and material handling logistics involves the movement, protection, and storage of goods within a logistics warehouse or during logistics transport. This logistics function ensures that items are securely handled and transported, preserving product quality. It is closely tied to inventory control, logistics warehouse operations, and overall logistics management. Additionally selecting cost-effective handling equipment improves efficiency and reduces labour costs.
Inventory Control in Logistics Management
Inventory control management is central to logistics services, ensuring that stock levels are adequate to meet customer orders while minimising excess. Effective inventory control reduces costs, supports order fulfilment, and enhances logistics coordination. By aligning inventory with market demand, logistics providers can create agile and flexible operations, especially in industries with short product life cycles.
Storage and Warehouse Logistics
Storage and logistics warehouse management focuses on optimising the placement and organisation of goods. This logistics function ensures easy access to products for packing and shipping, directly affecting order fulfilment. Efficient warehouse logistics reduce labour costs, improve inventory turnover, and enhance overall logistics management. The integration of warehouse management systems (WMS) and automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) further improves inventory accuracy and logistics services.
Transportation and Delivery Management in Logistics
Logistics transport and delivery management are crucial aspects of logistics services. This logistics function involves selecting transport modes, managing routes, and controlling transportation costs. It ensures timely and cost-efficient delivery, integrating with other logistics functions like inventory control and warehouse logistics. Advanced supply chain analytics allow logistics coordinators to monitor shipments in real-time, optimising logistics transport efficiency.
Product Packaging in Logistics
Product packaging plays an integral role in logistics management, ensuring that products are protected during logistics transport and stored appropriately within logistics warehouses. Effective packaging not only safeguards goods but also contributes to labour efficiency in material handling and storage. Tailoring packaging to regulatory requirements streamlines logistics services by preventing delays and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Supply Chain Data and Monitoring with Software
Logistics management increasingly relies on software tools for tracking and analysing logistics functions. Inventory management software and advanced analytics provide insights into inventory levels, replenishment planning, and logistics transport efficiency. Real-time data helps logistics providers optimise inventory control, logistics warehouse operations, and transportation management, driving better decision-making and improving overall logistics services.
Key Advantages of Logistics Management Functions
Logistics management functions are far from being a collection of disconnected tasks; they are, in fact, a cohesive framework that forms the backbone of any effective logistics operation. Their successful execution is a critical factor in determining a company’s ability to thrive and remain competitive in the modern marketplace.
The Impact of Effective Implementation
The true power of logistics management functions lies in their ability to enhance operational efficiency and drive down costs. When these processes are meticulously optimised, businesses can experience transformative benefits, including reduced waste, better resource allocation, and more efficient order fulfilment. The ripple effect of these improvements can significantly bolster a company’s profitability by streamlining workflows and maximising productivity.
Strengthening Supply Chain Expertise
Achieving proficiency within the supply chain through skillful logistics management results in a resilient and well-coordinated system, equipped to face a variety of challenges. This proficiency not only ensures that logistics costs remain under control but also facilitates flawless execution of the overall supply chain strategy. More importantly, it enables businesses to consistently meet customer expectations, establishing a foundation of reliability and trust.
Moreover, supply chain proficiency also extends to comprehensive risk management and mitigation efforts, which have become indispensable in navigating the uncertainties of today’s volatile global market.
Ensuring Timely Deliveries and Customer Satisfaction
At the core of logistics management lies the crucial role it plays in overseeing deliveries and maintaining customer satisfaction. By focusing on prompt order processing, effective transportation management, and precise inventory control, businesses can fulfill customer expectations with ease and consistency. This reliability is essential for building lasting customer relationships and fostering brand loyalty.
Ensuring Product Quality Throughout the Supply Chain
The quality of logistics management directly influences the final product that reaches the consumer. By carefully managing each phase—from inbound logistics to outbound fulfilment—companies can ensure that every step is executed with precision, resulting in high-quality products that meet or exceed customer expectations. This attention to detail not only enhances customer satisfaction but also strengthens the brand’s reputation in an increasingly competitive market.

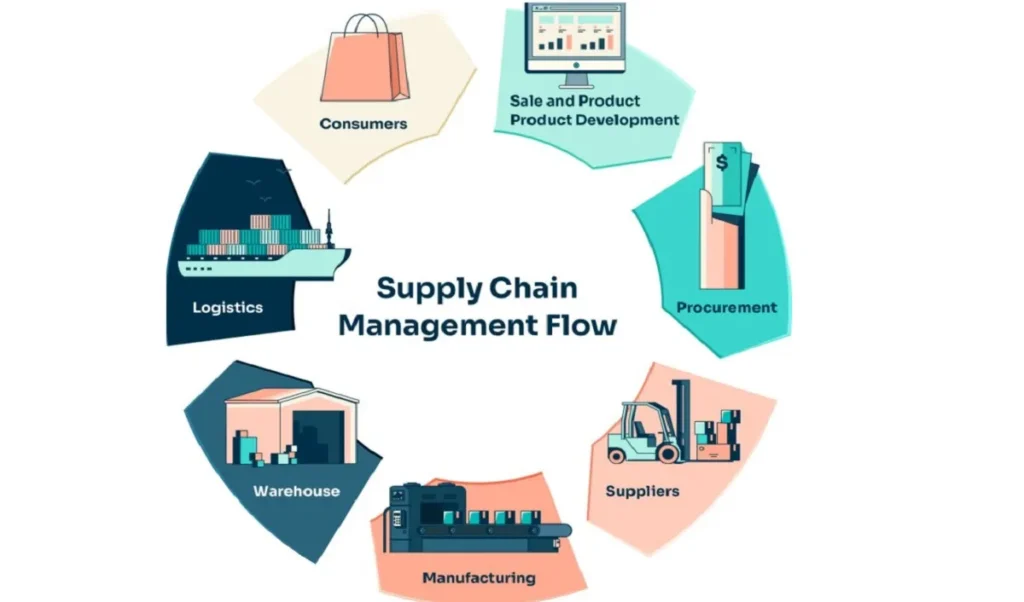
Optimising Logistics Management Functions Within Supply Chain Management
Logistics management functions (LMF) and supply chain management (SCM) are closely related but serve distinct purposes within the broader business operation.
LMF specifically deals with the detailed, tactical processes involved in the flow and storage of goods. It is primarily concerned with ensuring that products are transported efficiently, stored securely, and delivered promptly. The key tasks under logistics management include transportation planning, warehousing, inventory management, and order fulfilment. Essentially, LMF focuses on optimising the physical movement and handling of products from one point to another within the supply chain.
On the other hand, SCM covers a much broader spectrum, overseeing the entire flow of goods and services from raw material sourcing to delivering finished products to the end customer. SCM involves managing relationships with suppliers, overseeing production processes, and ensuring that all functions within the supply chain work in harmony to maximise customer value. SCM aims to coordinate all the elements involved in producing and distributing products, from procurement and manufacturing to logistics and customer service.
Integrating logistics management functions into the broader SCM framework is critical for operational efficiency. When logistics is aligned with the overall supply chain strategy, it enables businesses to reduce costs by optimising transportation routes, improving storage practices, and minimising inventory holding costs. Furthermore, it enhances delivery effectiveness, ensuring that products reach customers on time and in good condition. As a result, customer satisfaction improves, creating a competitive advantage for the business.
By integrating LMF into SCM, companies can create a seamless flow of goods, reduce operational redundancies, and boost overall performance, leading to long term business success.
To get more insights on supply chain management you may take a look at our courses on supply chain management.
Conclusion
Logistics management functions are key components of the supply chain, each contributing to the timely and cost effective delivery of products. They are critical for fulfilling customer demands and maintaining supply chain efficiency.
By optimising these functions, businesses can reduce costs, improve delivery performance, and enhance customer satisfaction—essential elements for gaining a competitive edge and ensuring long-term success in the marketplace.
Resources
Some related courses:
FAQ
Logistics is the management of moving and storing goods or information from one place to another, ensuring timely and efficient delivery. It involves transportation, warehousing, and inventory control.
Effective logistics management ensures timely delivery of products, reduces costs, enhances customer satisfaction, and improves overall supply chain efficiency.
The key components include transportation, warehousing, inventory management, packaging, order fulfilment, and supply chain coordination.
Technology like GPS tracking, warehouse management systems (WMS), and automated inventory control can streamline processes, improve accuracy, and provide real-time data for better decision making.
All Courses
Personal Development
640
Employability
402
Health & Care
318
Management
302
IT & Software
274
Business
263
Quality Licence Scheme Endorsed
252
Safety & First Aid
213
Teaching & Education
162
Accounting & Finance
146
Design & Technology
120
Construction & Engineering
116
Mental Health & Counselling
116
Sales & Marketing
111
Compliance & Law
97
Food & Nutrition
83
Science
71
Sports & Fitness
55
Language
50
Animal Care
41
Photography & Lifestyle
37
Makeup & Beauty
26
Programming & Coding
19
Cybersecurity
17
Business Communication
15
Career Bundle
14
Job Ready Programme
14
Development
10
Organizational Development
9
Leadership Development
8
Risk Management
6








0 responses on "Logistics Management: Definition, Functions, and Benefits"